At What Age Do Cataracts Start
Cataracts, a common eye condition that affects almost everyone as they age, often go unnoticed until our 60s or 70s. We may start experiencing more...
3 min read
Holli Richardson : Jul 24, 2019 2:12:48 PM


Systemic inflammation is a far too common problem posing a serious threat to human health. It’s estimated that the number of people with chronic inflammation diseases, such as diabetes, heart disease, and arthritis, will continue to increase for the next 30 years. Fortunately, dietary and lifestyle changes are often helpful for alleviating these health problems.
There are two types of inflammation: acute and chronic. Acute inflammation occurs when the body releases defensive chemicals and immune cells in response to injury or harmful bacteria; this type only lasts a few days. On the other hand, chronic inflammation can last for years and affects the entire body system, which is why it’s referred to as systemic inflammation. Chronic inflammation can result from allergies, food intolerances, exposure to toxins, nutrient deficiencies, excess fat tissue, and autoimmune disorders.
Systemic inflammation affects every part of the body, including your eyes, where it can contribute to macular degeneration and cataracts. In other areas of the body, the damage is just as severe. Immune cells can damage the digestive systems and cause IBS or interfere with metabolism and lead to weight gain. Inflammatory cells can promote the buildup of plaque in blood vessels, increasing the likelihood of heart attack and stroke. Chronic inflammation has further been linked to an increased risk of cancer and heart disease. In the brain, inflammation can cause brain fog, depression, fatigue, and headaches, among other problems.
Common signs of chronic inflammation include:
While over-the-counter medications can help reduce pain associated with temporary inflammation, John Hopkins Health Review stresses that these aren’t meant to treat chronic inflammation. Anti-inflammatory drugs may help, but they come with many problematic side effects. Instead, take a holistic approach to manage inflammation.
If you want to tackle inflammation at the cellular level, you’ll have to make some lifestyle changes. This involves removing inflammation triggers from your diet and engaging in activities that reduce systemic inflammation. Refined carbs, sugar, processed foods, trans fats, vegetable oils, and excessive alcohol consumption have all been found to promote inflammation. On the other hand, people who eat nutrient-dense diets high in antioxidants and healthy fats tend to have much lower levels of inflammation — the Mediterranean diet is often praised for this. You should also maintain the health of your gut. An unhealthy gut can cause inflammation, so make sure to care for it by eating foods rich in probiotics, including sauerkraut, yogurt, and apple cider vinegar.
Regular exercise is also vital for lowering inflammation. One study found that a 20-minute exercise session was enough to produce an anti-inflammatory response. These workout sessions don’t have to be intense — participants in the study simply walked on a treadmill!
CBD oil, for example, is gaining traction as an effective treatment for chronic inflammation. According to Medical News Today, recent research suggests that CBD can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain associated with inflammatory diseases like arthritis. Talk to your doctor about using CBD oil to manage your inflammation. Just be sure to do your research before making a purchase — sites like Remedy Review can help you find a quality CBD oil from a brand you can trust by breaking down the benefits of each product. Natural treatments for pain relief, such as CBD oil, are preferable over prescription pain medications. However, it’s still important to tackle the root cause of your inflammation.
It’s not just what you do during the day that matters. While we sleep, our bodies regulate the production of inflammatory cells. Getting the right amount of sleep is crucial for protecting yourself from the health issues that come with inflammation. Research has found that too little sleep, poor quality sleep, and too much sleep can contribute to inflammation. Try to get between seven and eight hours of sleep to help your body fight inflammation during the night.
Chronic inflammation can really put a damper on your quality of life. Inflammation is often the culprit behind many physical and mental issues, from chronic pain and depression to life-threatening diseases. Fortunately, making healthy lifestyle choices is a tried and true method of alleviating inflammation and finding relief from its associated health problems.
Written by guest blogger Holli Richardson of hollistics.net

Cataracts, a common eye condition that affects almost everyone as they age, often go unnoticed until our 60s or 70s. We may start experiencing more...
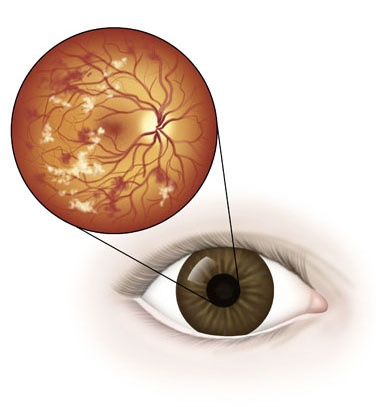
Diabetes is a disease that profoundly affects many areas of your body, including your eyes. It increases your risk for eye conditions, such as ...

If you take an honest assessment of your overall health and come to find that it’s not as good as it could be, you’re selling yourself short. We all...