Glaucoma
Leading Cause of Blindness
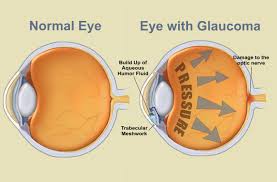
Glaucoma is a series of diseases that cause damage to the optic nerve.
Glaucoma is a series of diseases which damage the optic nerve, causing blind spots in the field of vision. Estimates are that glaucoma affects 1 in every 50 adults. The risk of developing glaucoma increases after age 35, though it can occur at any age.
When overproduction of eye fluids occurs, or when the eye’s drainage system becomes blocked, the increase in Glaucomapressure in the eye can cause damage to the optic nerve, resulting in glaucoma and permanent loss of vision.
In the most common type of glaucoma, early symptoms are often unnoticeable, with no discomfort or pain. Consequently, most people do not detect a problem until there has been a significant loss of vision. At later stages, central vision becomes affected, and can be accompanied by mild headaches and night vision difficulties. Some forms of the disease may include more noticeable symptoms such as blurred vision, severe pain, nausea, and halos around lights.
Glaucoma is generally detected in routine eye examinations where special instruments measure fluid pressure in the eye, and drainage channels are examined for proper fluid outflow. Left untreated, glaucoma causes total blindness.
Glaucoma cannot be cured, and lost vision cannot be restored. But early detection and treatment can usually control the disease and preserve vision. That’s why regular eye exams are crucial for those over age 35 or in other high risk groups. Treatment options available in our office for glaucoma include laser procedures.